Synchronous (blocking) interface
For simple access to a robot, one can use a synchronous (blocking) interface. This interface is
robot object obtained by get_robot() method
where argument coro is set to False (default). All members of this robot object are
designed to wait (block) till the command is completed. For example
play_note() plays a note and waits till the note is played.
Next command is executed after the previous one finishes.
- class ozobot.advanced.Bot(impl)
Ozobot main class
This class represents ozobot itself. Exactly one instance of this class matches to exactly one robot (an ozobot, in this case).
Class should be obtained by the
get_robot()getter.- Example
# Get default robot instance import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot()
- light_effects
Robot
LED lightscontrol interface
- sounds
Robot
sound systemcontrol interface
Robot
navigationcontrol interface for line following
- uuid
Robot UUID (if available) or
None
Robot LED lights
- class ozobot.advanced.BotLightEffects(impl)
This class represents access to robot LED lights. Instance of this class allows the user to set various LED lights colors, switch them ON and OFF or regulate lights intensity.
Note
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get an instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface of robot sound system import ozobot lights = ozobot.get_robot().light_effects
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
BotLightEffectsAsync- set_light_color(color, lights=Lights.ALL_ROBOT)
Set selected lights to a specific color according to enum.
- Parameters
color (
SurfaceColor) – Color to be displayed
- Example
# Set top and first front LED to RED color import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.light_effects.set_light_color(ozobot.SurfaceColor.RED, ozobot.Lights.FRONT_1 | ozobot.Lights.TOP)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aset_light_color
- set_light_color_rgb(red, green, blue, lights=Lights.ALL_ROBOT)
Set selected lights to a specific RGB color
Set selected lights according to a specific RGB color. Apply command over all lights when last argument is omitted.
- Parameters
- Example
# Set first and second front LED to 20% of GREEN color import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.light_effects.set_light_color_rgb(0.0, 0.2, 0.0, ozobot.Lights.FRONT_1 | ozobot.Lights.FRONT_2)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aset_light_color_rgb
Robot sound system
Basic sounds
- class ozobot.advanced.BotSounds(impl)
This class represents access to the robot’s sound system interface. Instance of this class allows the user to play various types of sounds such as tones, notes or emotion sounds or numbers.
Note
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get an instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface of robot sound system import ozobot sound = ozobot.get_robot().sound
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
BotSoundsAsync- emotions
Robot
emotions sounds
- play_tone(freq, duration)
Play a tone of a specific frequency for a certain time.
- Parameters
freq (
int) – Frequency to be playedduration (
float) – Duration in seconds
:example:shall
# Play 1kHz for 400 milliseconds import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.play_tone(1000, 0.4)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_tone
- play_note(octave, note, duration)
Play a specific note of a specific octave for a certain time. Standard pitch notation is uded, i.e. A4 = 440 Hz.
- Parameters
octave (int) – Octave number in range -1 .. 10
note (ozobot.Note) – Note to be played
duration (float) – Duration in seconds
- Example
#Play note G2 for 400 milliseconds import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.play_note(2, ozobot.Note.G, 0.4)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_note
- play_midi_note(midi_note_number, duration)
Play a specific note according to MIDI specification.
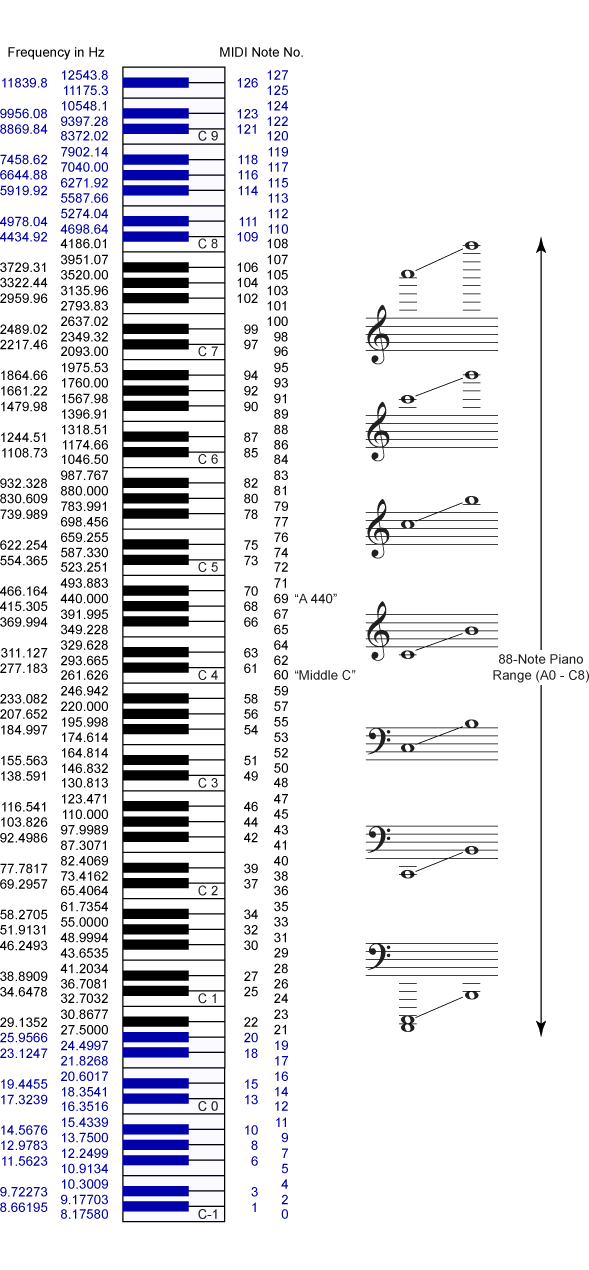
- Parameters
midi_note_number (
int) – MIDI note number (see picture above)duration (
float) – Duration in seconds
- Example
# Play note A4 for 2 seconds import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.play_midi_note(69,2)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_midi_note
- say_color(color)
Pronounce the name of the color obtained as a color ID.
- Parameters
color (ozobot.SurfaceColor) – Color enumerator
- Example
# Say green import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.say_color(ozobot.SurfaceColor.GREEN)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
asay_color
- say_direction(direction)
Pronounce the name of the obtained direction.
- Parameters
direction (ozobot.Directions) – Directions enumerator
- Example
# Say forward and left import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.say_direction(ozobot.Directions.FORWARD | ozobot.Directions.LEFT)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
asay_direction
- say_number(number)
Pronounce the number.
- Parameters
number (
int) – Number to say (in range -199 to 199)- Example
# Say answer to the Ultimate Question of Life, the Universe, and Everything import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.say_number(42)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
asay_number
- stop_audio()
Stop any audio that is being played.
- Example
# Stops currently playing sound import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.stop_audio()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
astop_audio
Emotions sounds
- class ozobot.advanced.BotSoundsEmotions(impl)
This class represents access to the robot’s emotion sound interface. Instance of this class allows the user to play various emotion sounds such as happy, sad, surprised and so on.
Note
This instance should not be created by the user, but it should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get an instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface of the robot emotions sound system import ozobot emotions = ozobot.get_robot().sound.emotions
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
BotSoundsEmotionsAsync- play_happy()
Play a sound representing the robot’s happy emotion.
- Example
# Play happy sound import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.emotions.play_happy()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_happy
- play_sad()
Play a sound representing the robot’s sad emotion.
- Example
# Play sad sound import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.emotions.play_sad()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_sad
- play_surprised()
Play a sound representing the robot’s surprised emotion.
- Example
# Play surprised sound import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.emotions.play_surprised()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_surprised
- play_laugh()
Play a sound representing the robot’s laugh emotion.
- Example
# Play laugh sound import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.sounds.emotions.play_laugh()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aplay_laugh
Robot movement
- class ozobot.advanced.BotMovement(impl)
This class represents access to robot movement system interface. Instance of this class allows the user to move or rotate the robot.
Note
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface of robot movement system import ozobot movement = ozobot.get_robot().movement
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
BotMovementAsync- move(distance, speed)
Move the robot by a certain distance at a certain speed.
- Parameters
distance (
float) – Move distance in metersspeed (
float) – Move speed in meters per second
- Example
# Move the robot 10 centimeters # at speed 2 centimeters per second import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.movement.move(0.1, 0.02)
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
amove
- rotate(angle, speed)
Rotate the robot by a certain angle at a certain angular speed.
- Parameters
angle (
float) – Angle to rotate in radiansspeed (
float) – Angular speed in radians per second
- Example
# Rotate robot by 180 degrees at a speed of 90 degrees per second import ozobot from math import radians bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.movement.rotate(radians(180), radians(90))
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
arotate
- set_velocity(forward_speed, angular_speed)
Set velocity of the robot by setting forward speed and angular speed.
- Parameters
forward_speed (
float) – Forward speed of the robot in meters per secondangular_speed (
float) – Angular speed of the robot in radians per second
- Example
# Run robot in a circle import ozobot from math import radians bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.movement.set_velocity(0.003, radians(5))
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
aset_velocity
- stop_motors()
Stop robot’s movement immediately (break).
- Example
# Run robot in circles import ozobot bot = ozobot.get_robot() bot.movement.stop_motors()
See also
There is also an asynchronous coroutines based variant
astop_motors
Asynchronous (coroutine) interface
This interface provides the same functionality as Synchronous (blocking) interface, but
provides so called Coroutines instead of standard blocking methods. These
Coroutines are designed to be able to be used with asyncio module
which provides an interface for Cooperative scheduling in Python.
- class ozobot.advanced.BotAsync(impl)
Ozobot main class - coroutines variant
Coroutines variant of
Bot- Warning
Please don’t construct this object directly as its implementation may differ across platforms. Rather use
get_robot()getter function instead.- light_effects
Robot
LED lightscontrol interface
- sounds
Robot
sound systemcontrol interface
Robot
navigationcontrol interface for line following
- uuid
Robot UUID (if available) or
None
Robot LED lights (coroutines)
- class ozobot.advanced.BotLightEffectsAsync(impl)
This class is the asynchronous variant of
BotLightEffectsNote
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get an instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface for robot light effects import ozobot lights = ozobot.get_robot(coro = True).light_effects
- async aset_light_color(color, lights=Lights.ALL_ROBOT)
Coroutine variant of
set_light_color().- Parameters
color (
SurfaceColor) – Color to be displayed
- Example
# Show a kind of rainbow from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, Lights, SurfaceColor async def task(delay_ms): bot = get_robot(coro = True) lights = ((Lights.FRONT_1, 0), (Lights.FRONT_2, 1), (Lights.FRONT_3, 2), (Lights.FRONT_4, 3), (Lights.FRONT_5, 4)) colors = (ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK, ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK, ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK, ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK, ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK, ozobot.SurfaceColor.RED, ozobot.SurfaceColor.YELLOW, ozobot.SurfaceColor.GREEN, ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLUE, ozobot.SurfaceColor.MAGENTA) cnt = len(colors) for i in range(cnt * 4): for l in lights: await bot.light_effects.aset_light_color(colors[(l[1] + i) % cnt], l[0]) await asyncio.sleep_ms(delay_ms) await bot.light_effects.aset_light_color(ozobot.SurfaceColor.BLACK) asyncio.run(task(300))
- async aset_light_color_rgb(red, green, blue, lights=Lights.ALL_ROBOT)
Coroutine variant of
set_light_color_rgb().- Parameters
- Example
# Show a kind of rainbow from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, Lights from math import sin, pi async def task(delay_ms): bot = get_robot(coro = True) pi4 = pi / 4 lights = ((Lights.FRONT_1, 0 * pi4), (Lights.FRONT_2, 1 * pi4), (Lights.FRONT_3, 2 * pi4), (Lights.FRONT_4, 3 * pi4), (Lights.FRONT_5, 4 * pi4)) for i in range(8192): for l in lights: a = i / 256 + l[1] await bot.light_effects.aset_light_color_rgb(sin(a), sin(a + pi4), sin(a + pi4 * 2), l[0]) await asyncio.sleep_ms(delay_ms) await bot.light_effects.aset_light_color(SurfaceColor.BLACK) asyncio.run(task(1))
Robot sound system (coroutines)
Basic sounds (coroutines)
- class ozobot.advanced.BotSoundsAsync(impl)
This class is the asynchronous variant of
BotSoundsThis instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface for robot sound system import ozobot sound = ozobot.get_robot(coro = True).sound
- emotions
Robot
emotions sounds
- async aplay_tone(freq, duration)
Coroutine variant of
play_tone().- Parameters
freq (
int) – Frequency to be playedduration (
float) – Duration in seconds
- Example
# Play sirene from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio async def task(delay, cnt): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for i in range(cnt): for freq in range(50, 200): asyncio.create_task(sounds.aplay_tone(freq * 20, delay * 2)) await asyncio.sleep(delay) for freq in reversed(range(50, 200)): asyncio.create_task(sounds.aplay_tone(freq * 20, delay * 2)) await asyncio.sleep(delay) await sounds.astop_audio() # Delay between changes 10ms repeated 4-times asyncio.run(task(0.01, 4))
- async aplay_note(octave, note, duration)
Coroutine variant of
play_note().- Parameters
octave (int) – Octave number in range -1 .. 10
note (ozobot.Note) – Note to be played
duration (float) – Duration in seconds
- Example
# Play Forrest Gump theme from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, Note octave = 4 speed = 1.8 notes = ((Note.E, 0, 1/8), (Note.F, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/4), (Note.E, 0, 1/4), (Note.G, 0, 1/4), (Note.C, 1, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/4), (Note.E, 0, 1/4+1/8), (Note.F, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/8), (Note.A, 0, 1/8), (Note.A, 0, 1/4), (Note.F, 0, 1/4), (Note.A, 0, 1/4), (Note.F, 1, 1/8), (Note.E, 1, 1/8), (Note.D, 1, 1/8), (Note.C, 1, 1/8), (Note.A, 0, 1/8), (Note.F, 0, 1/8), (Note.F, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/8), (Note.A, 0, 1/8), (Note.A, 0, 1/4), (Note.F, 0, 1/4), (Note.A, 0, 1/4), (Note.D, 1, 1/8), (Note.B, 0, 1/4), (Note.G, 0, 1/4+1/8), (Note.E, 0, 1/8), (Note.F, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/4), (Note.C, 1, 1/8), (Note.G, 0, 1/4+1/2)) async def play_note(sounds, note, oct, delay): await sounds.aplay_note(oct + octave, note, delay * speed) async def task(notes): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for note in notes: await play_note(sounds, *note) # Play theme asyncio.run(task(notes))
- async aplay_midi_note(midi_note_number, duration)
Coroutine variant of
play_midi_note().- Parameters
midi_note_number (
int) –MIDI note number (see MIDI specification)
duration (
float) – Duration in seconds
- Example
# Play Forrest Gump theme from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio transpose = 65 speed = 1.8 midi = ((0, 1/8), (1, 1/8), (3, 1/8), (3, 1/4), (0, 1/4), (3, 1/4), (8, 1/8), (3, 1/4), (0, 1/4+1/8), (1, 1/8), (3, 1/8), (5, 1/8), (5, 1/4), (1, 1/4), (5, 1/4), (13, 1/8), (12, 1/8), (10, 1/8), (8, 1/8), (5, 1/8), (1, 1/8), (1, 1/8), (3, 1/8), (5, 1/8), (5, 1/4), (1, 1/4), (5, 1/4), (10, 1/8), (7, 1/4), (3, 1/4+1/8), (0, 1/8), (1, 1/8), (3, 1/8), (3, 1/4), (8, 1/8), (3, 1/4+1/2)) async def play_note(sounds, note, delay): await sounds.aplay_midi_note(note + transpose, delay * speed) async def task(midi): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for tone in midi: await play_note(sounds, *tone) # Play theme asyncio.run(task(midi))
- async asay_number(number)
Coroutine variant of
say_number().- Parameters
number (
int) – Number to say in range -199 to 199- Example
# Count down from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio async def task(cnt = 3, delay = 0.5): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for i in reversed(range(cnt + 1)): await asyncio.sleep(delay) await sounds.asay_number(i) asyncio.run(task())
- async asay_color(color)
Coroutine variant of
say_color().- Parameters
color (ozobot.SurfaceColor) – Color enumerator
- Example
# Say all supported colors from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, SurfaceColor async def task(delay = 0.2): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for color in dir(SurfaceColor): color = getattr(SurfaceColor, color) if isinstance(color, SurfaceColor) and not color == SurfaceColor.UNKNOWN: await sounds.asay_color(color) await asyncio.sleep(delay) asyncio.run(task())
- async asay_direction(direction)
Coroutine variant of
say_direction().- Parameters
direction (ozobot.Directions) – Directions enumerator
- Example
# Say all directions from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, Directions async def task(delay = 0.2): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for color in dir(Directions): color = getattr(Directions, color) if isinstance(color, SurfaceColor) and not color == SurfaceColor.UNKNOWN: await sounds.asay_color(color) await asyncio.sleep(delay) asyncio.run(task())
- async astop_audio()
Coroutine variant of
stop_audio().- Example
# Say all directions from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, Directions async def task(delay = 0.2): sounds = get_robot(coro = True).sounds for color in dir(Directions): color = getattr(Directions, color) if isinstance(color, SurfaceColor) and not color == SurfaceColor.UNKNOWN: await sounds.asay_color(color) await asyncio.sleep(delay) asyncio.run(task())
Emotions sounds (coroutines)
- class ozobot.advanced.BotSoundsEmotionsAsync(impl)
This class is the asynchronous variant of
BotSoundsEmotionsNote
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get an instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface for robot light effects import ozobot emotions = ozobot.get_robot(coro = True).sounds.emotions
- async aplay_happy()
Coroutine variant of
play_happy().- Example
# Play 6 times laugh or happy sounds from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, random async def task(): bot = get_robot(coro = True) for i in range(6): if 0 == random.randrange(2): await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_laugh() else: await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_happy() asyncio.run(task())
- async aplay_sad()
Coroutine variant of
play_sad().- Example
# Play 4 times sad or surprised sounds from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, random async def task(): bot = get_robot(coro = True) for i in range(4): if 0 == random.randrange(2): await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_sad() else: await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_surprised() asyncio.run(task())
- async aplay_surprised()
Coroutine variant of
play_surprised().- Example
# Play 4 times sad or surprised sounds from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, random async def task(): bot = get_robot(coro = True) for i in range(4): if 0 == random.randrange(2): await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_sad() else: await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_surprised() asyncio.run(task())
- async aplay_laugh()
Coroutine variant of
play_laugh().- Example
# Play 6 times laugh or happy sounds from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio, random async def task(): bot = get_robot(coro = True) for i in range(6): if 0 == random.randrange(2): await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_laugh() else: await bot.sounds.emotions.aplay_happy() asyncio.run(task())
Robot movement (coroutines)
- class ozobot.advanced.BotMovementAsync(impl)
This class is the asynchronous variant of
BotMovementNote
This instance should not be created by the user, but should be obtained by
get_robot(). Use the following code to get instance of this object related to exact robot:# Get interface of robot movement system import ozobot movement = ozobot.get_robot(coro = True).movement
- async amove(distance, speed)
Coroutine variant of
move().- Parameters
distance (
float) – Move distance in metersspeed (
float) – Move speed in meters per second
- Example
# Square walk 10 x 10 centimeters from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio from math import radians async def task(distance, cnt): movement = get_robot(coro = True).movement angle = radians(90) for i in range(cnt * 4): await movement.amove(distance, 0.02) await movement.arotate(angle, angle) # Delay between changes 1ms repeated 4-times asyncio.run(task(0.1, 4))
- async arotate(angle, speed)
Coroutine variant of
rotate().- Parameters
angle (
float) – Angle to rotate in radiansspeed (
float) – Angular speed in radians per second
- Example
# Square walk 10 x 10 centimeters from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio from math import radians async def task(distance, cnt): movement = get_robot(coro = True).movement angle = radians(90) for i in range(cnt * 4): await movement.amove(distance, 0.02) await movement.arotate(angle, angle) # Delay between changes 1ms repeated 4-times asyncio.run(task(0.1, 4))
- async aset_velocity(forward_speed, angular_speed)
Coroutine variant of
set_velocity().- Parameters
forward_speed (
float) – Forward speed of robot in meters per secondangular_speed (
float) – Angular speed of robot in radians per second
- Example
# Move arc from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio from math import radians async def task(distance, cnt): movement = get_robot(coro = True).movement await bot.movement.aset_velocity(0.003, radians(5)) await asyncio.sleep(4) await bot.movement.astop_motors(0.003, radians(5)) # Delay between changes 1ms repeated 4-times asyncio.run(task(0.1, 4))
- async astop_motors()
Coroutine variant of
stop_motors().- Example
# Move arc from ozobot import get_robot, asyncio from math import radians async def task(distance, cnt): movement = get_robot(coro = True).movement await bot.movement.aset_velocity(0.003, radians(5)) await asyncio.sleep(4) await bot.movement.astop_motors(0.003, radians(5)) # Delay between changes 1ms repeated 4-times asyncio.run(task(0.1, 4))